
Teaching and learning resources for the construction industry with NVQ and Diploma Assessment Criteria
Unit 206 Construct cavity walling forming masonry structures
The aim of this unit is to provide the learner with the
knowledge and skills to construct walling to form masonry structures
The learner will:
Vertical Penetrating of Damp
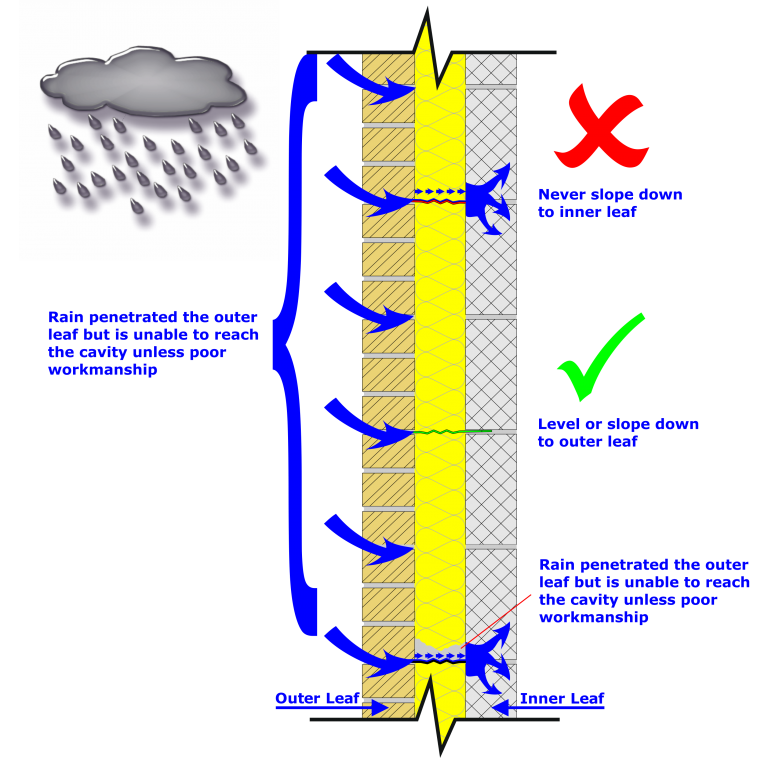
Whilst a horizontal D.P.C. stops damp rising up from the ground through your walls, a vertical D.P.C. is used to stop water travelling sideways through walls and surfaces that may come in contact with each other.
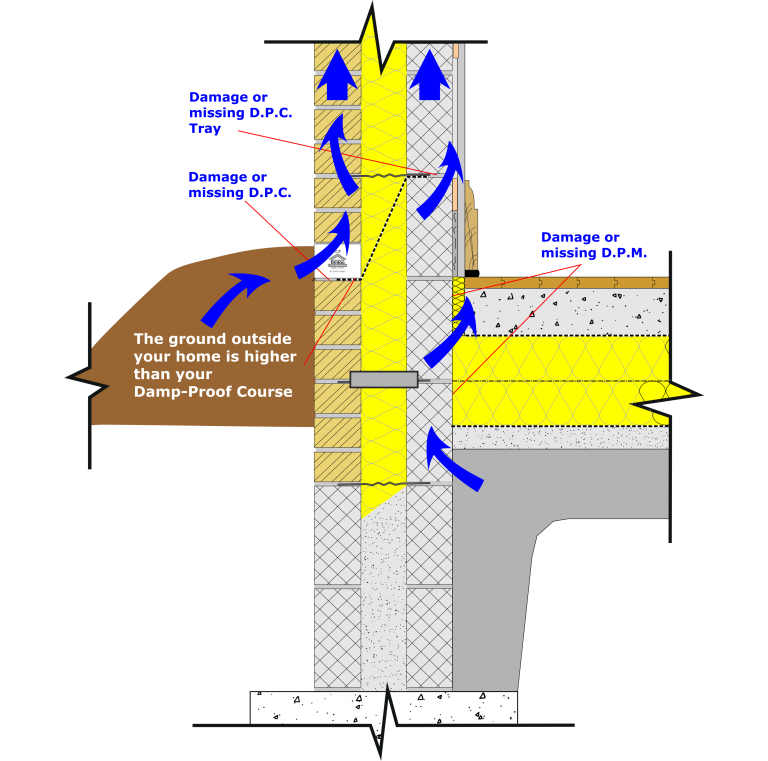
Rising Damp refers to moisture that is drawn upwards from ground level and below by a process known as capillary attraction.
A Horizontal Damp Proof Course installed at a minimum of 150mm above finished ground level is designed to halt the progress of rising damp.
The position of a Horizontal D.P.C. usually corresponds to F.F.L.
Rising Damp
Parapet
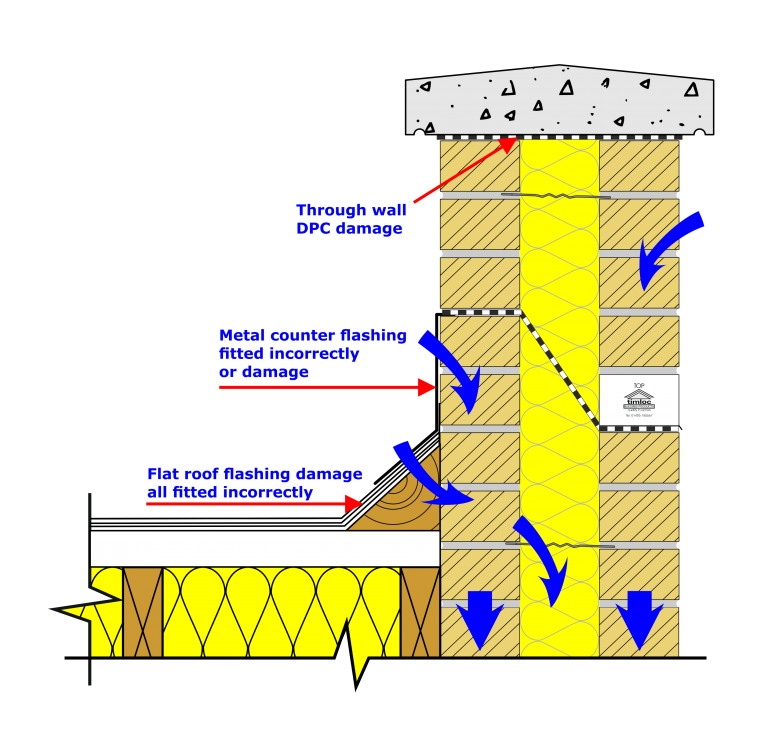
Another example but a less frequent point of moisture entry is where a cavity wall projects above a roofline in the form of a parapet.
Moisture can penetrate from above and this requires special DPC arrangements to protect the structure from damage.

Storing Flexible D.P.C.
Store damp-proof course (D.P.C.) materials in the dry and under cover, protect them against damage.
In addition, store flexible materials as follows.

Storing Flexible D.P.C.
• Stack rolls on end, no more than three rolls high.
• Rolls of D.P.C. that are stored flat are prone to distortion which can make them difficult to lay.
• If possible store at an even temperature.
• Ensure that bitumen and other thermoplastic materials are not in contact with any direct heat source.
• Since some D.P.C. materials may become stiff in cold weather conditions, store sufficient rolls for the next day’s use in a warm place overnight.
• Check the labels on adhesives for any storage requirements, eg avoidance of high or low temperature, and for any hazards relating to solvent vapours.

In all cases follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for storage and handling.
The most common types used are:

Polythene DPC

Pitch polymer DPC

Insulated DPC

Bitumen felt DPC
Roles of D.P.C. come in a range of widths from 110 to 300mm and supplied in lengths of 8 to 30m
Specialist types of flexible D.P.C. are also available in lead and copper coated with bitumen to prevent any corrosion and staining of the face brickwork which are more expensive.
A Horizontal Damp Proof Course (D.P.C.) is positioned in both internal and external leaves of a cavity wall at a level that is no lower than 150mm above finished ground level, as required by the Building Regulations.
Flexible D.P.C. is laid on to a fresh bed of mortar approximately 5mm thick and should cover the whole length and width of the wall.
The mortar bed should be free from stones that could penetrate the flexible D.P.C. causing rising damp through the rest of the internal or external leaf.
Placing the D.P.C. roll at one end of a wall, gently unrolled and pressed into the mortar using the back of the Brick Trowel so that the D.P.C. adheres to the mortar bed.
Overlapping or change in direction in a leaf the D.P.C. must overlap a minimum of 100mm or width of the D.P.C.
Ensure that the D.P.C. does not go into the cavity space causing obstruction and D.P.C. external edges are visible and not bridged by the mortar when completing the pointing.
The bed mortar which is underneath the flexible D.P.C. should have a flush finish with the flexible D.P.C. extending from the face of the wall.
Buildings built on sites that have sloping ground you need to take extra care and attention is needed to ensure that the D.P.C. is at 150mm minimum above-finished ground level.
The steps in horizontal D.P.C. should be multiples of 75mm and any overlapping should be done on the bed joint with a minimum of 100mm.
Damp Proof Membrane
Damp Proof Membrane (D.P.M.) is a membrane to ground moisture travelling through into the concrete slab
The membrane is laid on a layer of binding sand to prevent the membrane from getting punctured, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Damp Proof Membrane should be 1200 gauge and normally come in the lengths of 25m and 4m wide, with any overlapping, should be a minimum of 150mm.
To ensures continuous effective barrier against rising damp the D.P.M. is folded up and under the internal leaf D.P.C.
Good workmanship principles are needed to ensure that all junctions between the D.P.C. and D.P.M. are undamaged during the construction phase
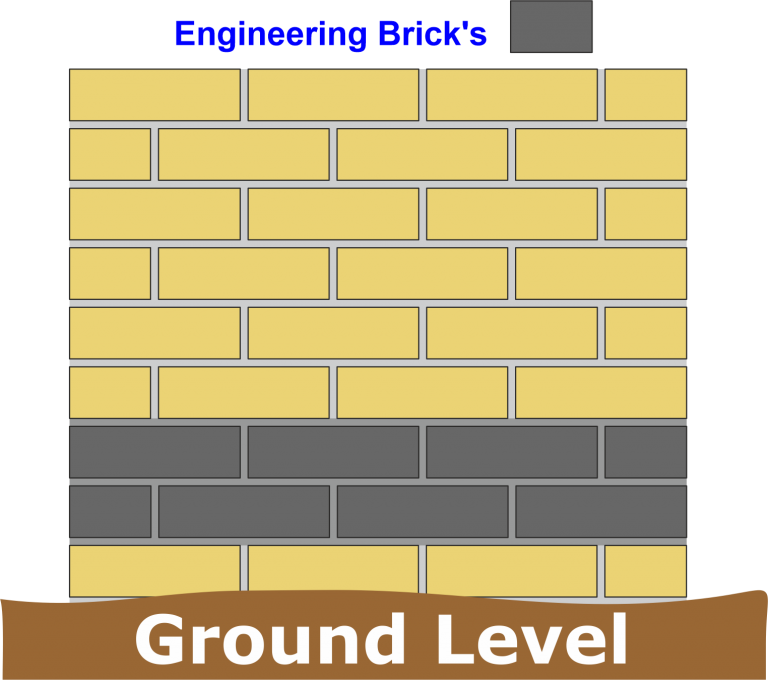
Rigid DPC
Rigid DPCs are suitable to resist the passage of rising damp but not the downward flow
of water.
The most common types of rigid DPC are:
• Two courses of engineering bricks bedded in a designated mortar.
• Two courses of slate bonded and bedded in a designated mortar.
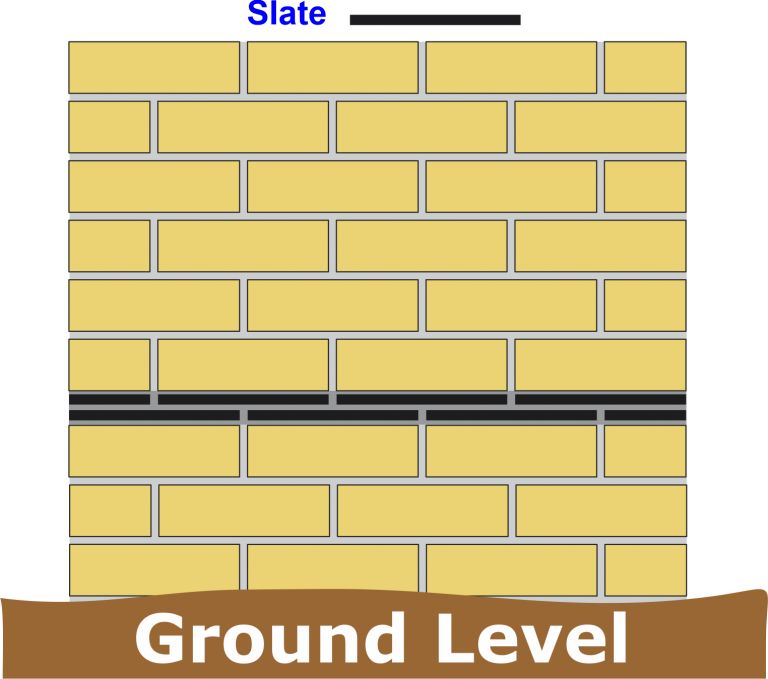

Rigid DPC
Portland cement or sulphate resistant Portland cement and lime, with or without air entrainment 1 of cement and 3 parts of sand.
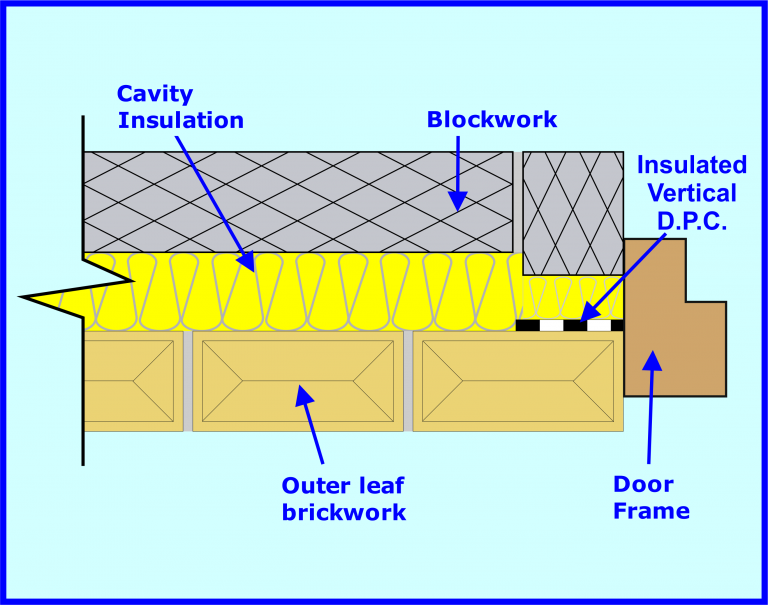
Vertical DPC
Whilst a horizontal D.P.C. stops damp rising up from the ground through your walls, a vertical D.P.C. is used to stop water travelling sideways through walls and surfaces that may come in contact with each other.
Vertical damp proof courses are usually installed around windows or doors when they are being installed in a cavity wall.
When new windows and doors are installed in a cavity wall, the cavity needs to be closed around the frame to secure the window or door properly
Closing the cavity forms the door or window reveals once this closure has then been plastered over.
The cavity closing around the window or door means that the external and internal walls come into contact with one another.
The vertical D.P.C. is inserted between the walls around the window to stop water travelling in from outside through the external wall from reaching the internal wall.
Vertical D.P.C.s are usually damp proof membranes, but laying a normal damp proof membrane intended for horizontal D.P.C. use isn’t actually sufficient for use as a damp proof course around windows, it is usually recommended to use an insulated D.P.C.
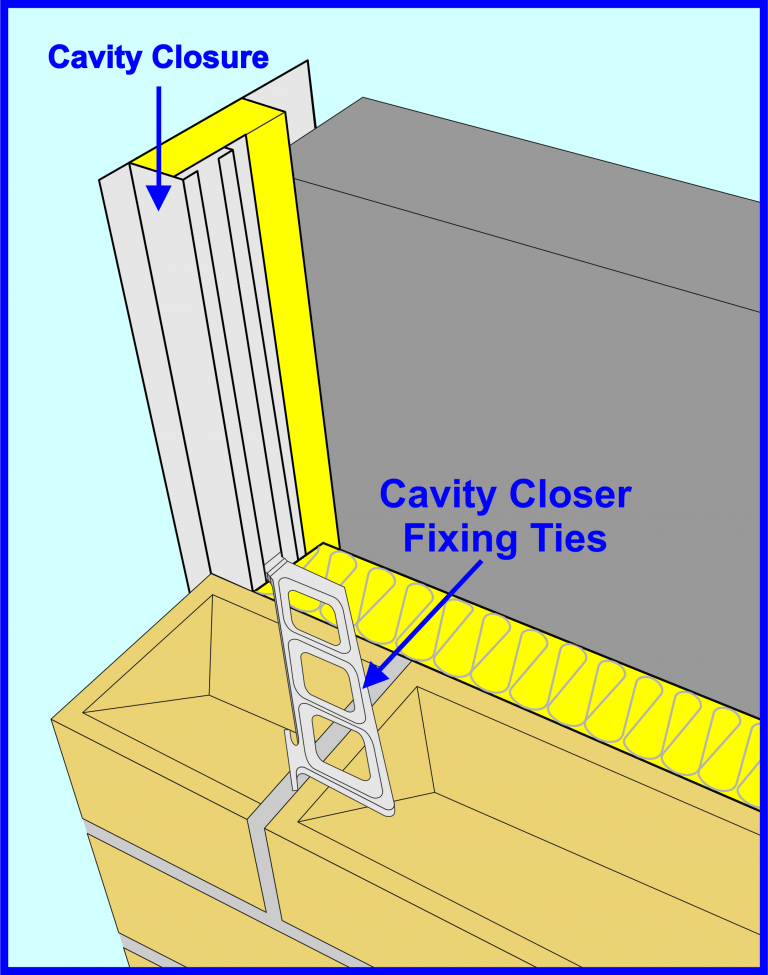
Detailed Drawing of a Cavity Closure
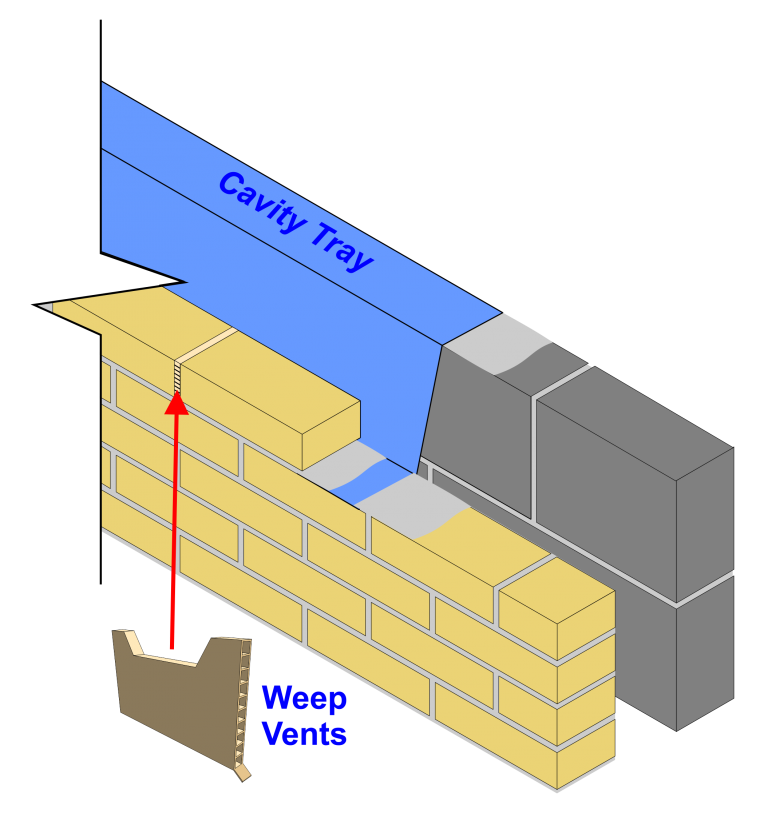
Example of Cavity Tray
D.P.C.’s and cavity tray should always be bedded onto fresh mortar, never dry bedded.
The masonry laid over the D.P.C. should also be bedded onto fresh mortar so that the D.P.C. is approximately halfway through the thickness of the mortar joint.
Ground floor level D.P.C.’s in external walls should be laid a minimum of 150mm above the adjacent ground level.
The D.P.C. must be at least as wide as the thickness of the wall.
If the D.P.C. is narrower, full protection cannot be achieved and moisture may track up the wall and past the D.P.C.
If joints are required within the material, they must be lapped by a minimum of 150mm, including onto any accessories, and all laps sealed using Jointing Tape..
Any situation where water must be discharged from an external wall, e.g:
At ground floor slab level
Within D.P.C. cavity tray systems every 900mm double check with specifications before starting work
Over external lintels for doors and windows every 450mm check specifications before starting work
Where a cavity must be ventilated
Weep Vent is used to drain lintels, cavity trays and to ventilate cavity walls.
To work effectively wall weeps should be placed directly on top of the base of a cavity tray or D.P.C., or on the front flange of the lintel Wall weeps should be spaced at 450mm centres to comply with NHBC recommendations
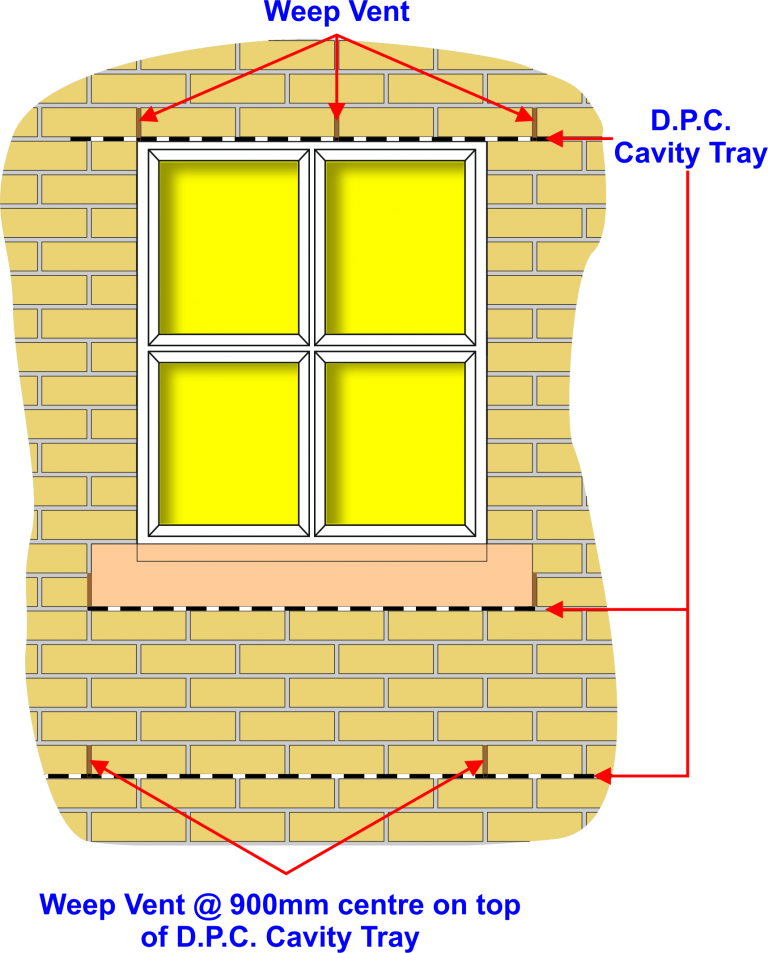
Position of Cavity Tray