
Teaching and learning resources for the construction industry with NVQ and Diploma Assessment Criteria
1.2 Identify the Materials required to build the following units in Brickwork Qualifications.
Unit 005 Constructing Half Brick Walling
Unit 118 Constructing Block Walling
Unit 119 Constructing Half Brick Return Corners
Unit 120 Constructing Cavity Walls in Brickwork & Block Work
Unit 121 Constructing One Brick Walling
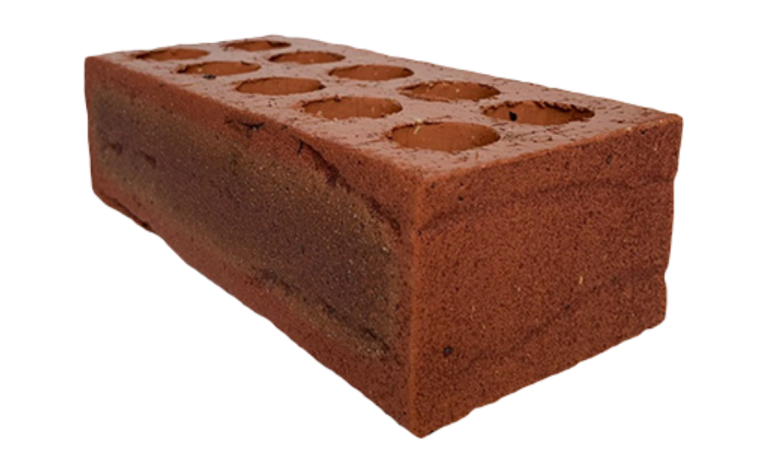

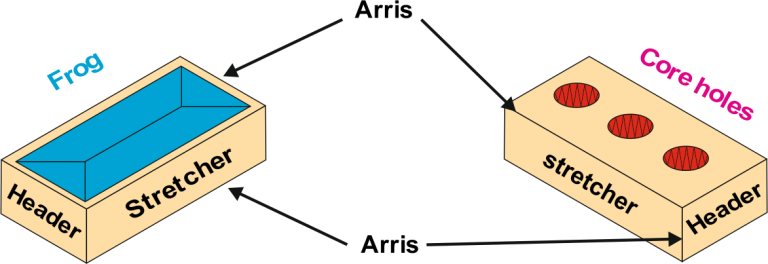
Face Brick

Engineering Brick

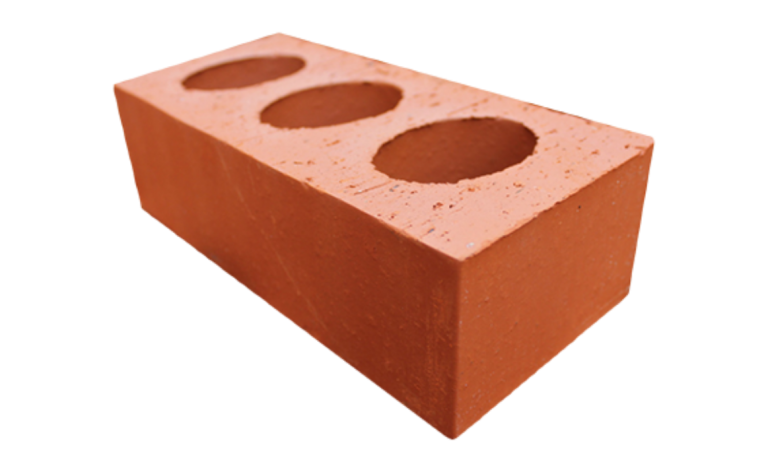
Common Brick
1. Facing Bricks are more expensive and are made from selected clays.
The face of bricks can vary in texture to give an attractive finish to walls.
2. Common Bricks are basic, cheaper bricks that are used mainly for internal walls, underground in foundations or external walls that will be rendered or clad.
3. Engineering Bricks are heavy, very strong and do not absorb water.
They are used where there are heavy loads, e.g. bridges, and in damp conditions such as inspection chambers, basements and other kinds of work below ground.
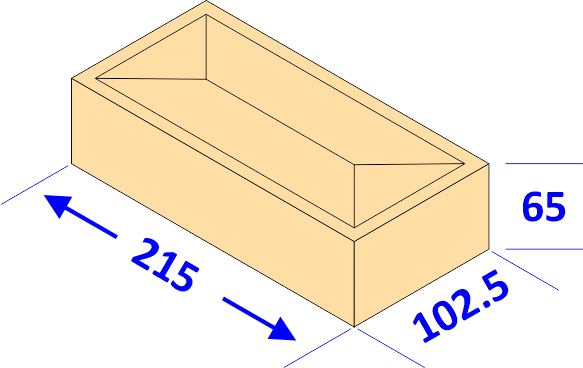
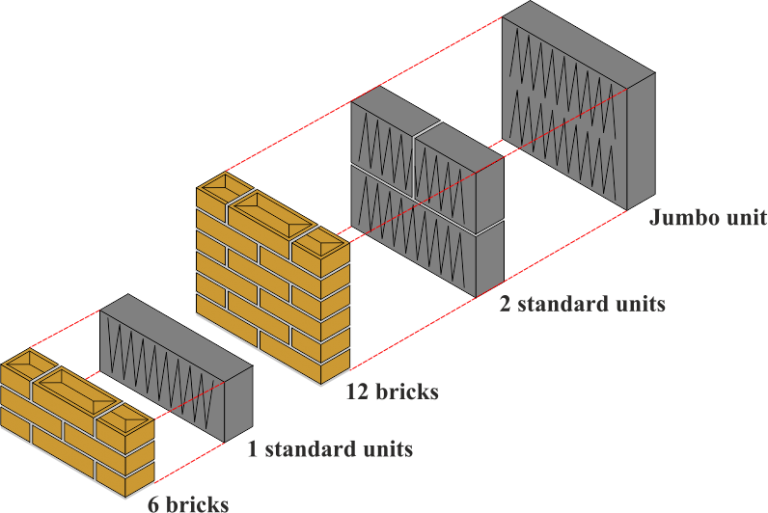
Brick Working Size
Working size of metric clay bricks is approximately 215×102.5×65mm, the size is not set in stone because the clay is a naturally occurring material and variations in drying and shrinking means that actual dimensions can vary.
For additional information on this topic click on the links below
Lightweight Block
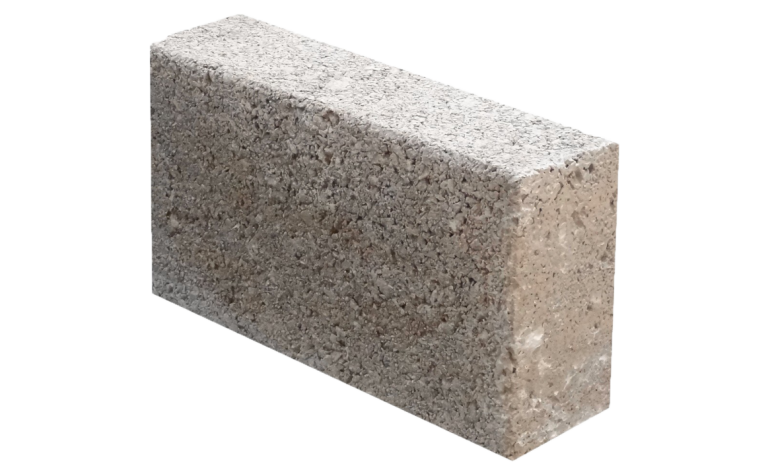

Lightweight Block
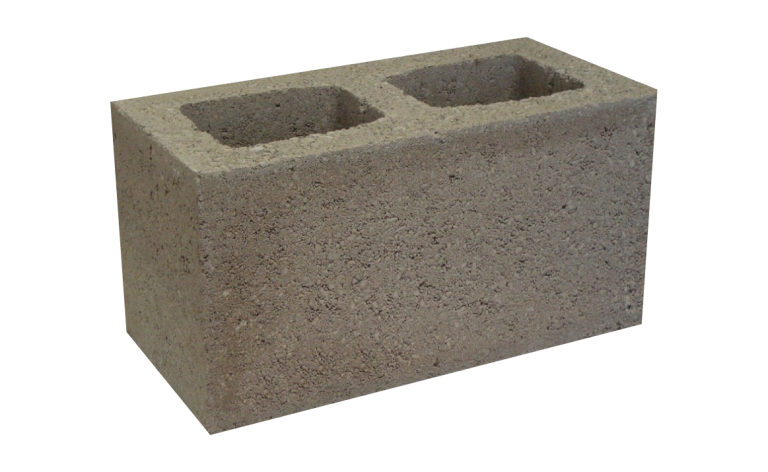

Hollow Block
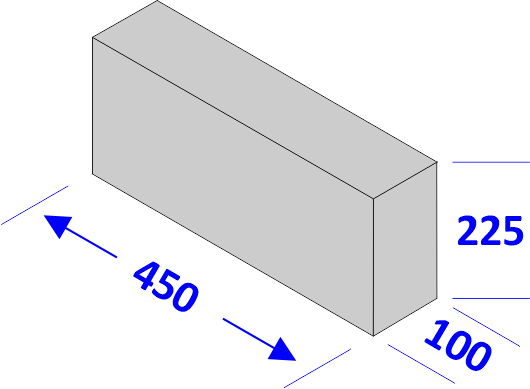
Blocks are produced in a broad range of sizes, but for general building work the most commonly used is referred to as a standard block and measures 440mm x 100mm x 215mm.
For additional information on this topic click on the links below
Brick and blocks are laid to different thicknesses this will depend on the type of wall you are building.
The correct term is half or one brick wall see examples below
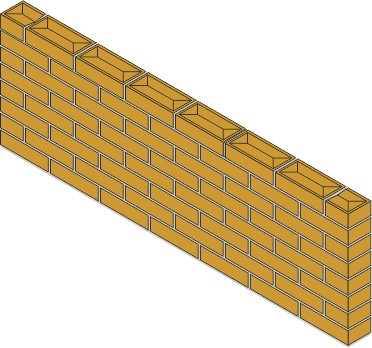
Half Brick Stretcher Bond
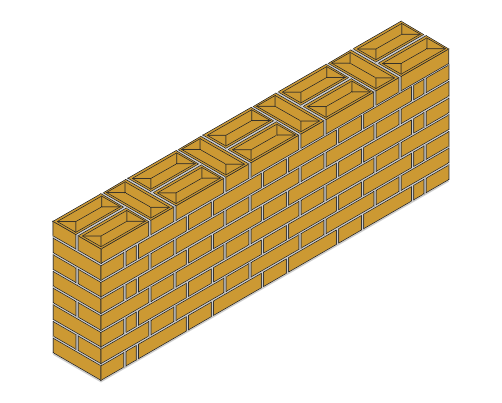
One Brick Flemish Bond
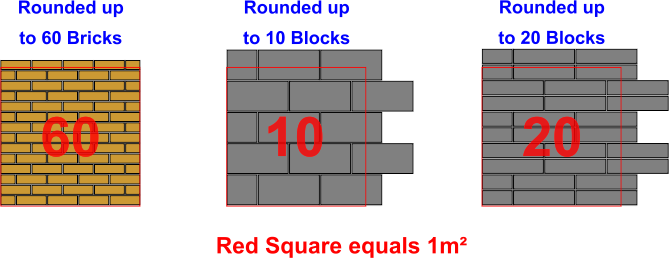
The half brick wall has 60 bricks per 1m²
One brick wall has 120 bricks per 1m², normally a garden walls.
½ brick wall is referred to as an outer or inner leaf when constructing a cavity wall.
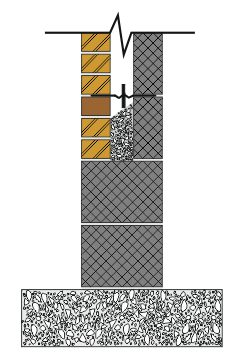
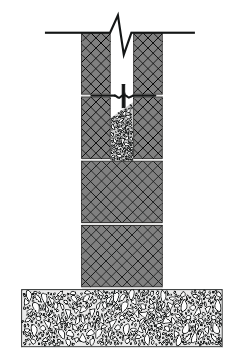
A cavity wall can be built out of concrete blocks completely, or the inner leaf with concrete blocks and the outer leaf in bricks.
There are 10 concrete blocks per 1m² for a single skin wall, for cavity wall which is built out of concrete blocks completely this will be 20 blocks per 1m²
For additional information on this topic click on the links below

DPC Rigid Bitumen Felt
Damp Proof Course (D.P.C.) is a material that is impervious to water penetration which stops the moisture from entering the main structure of the building.
There are two main types of D.P.C. materials used, Flexible or Rigid.
A Damp Proof Course is an essential part of a cavity wall design and will be positioned in several locations in a structure.
Without a correctly positioned D.P.C., the ability of the cavity wall to prevent moisture from entering into the living or working area of a structure will be severely compromised.
Moisture, or ‘damp’ as it’s more commonly referred to, enters a cavity wall in several ways, here are a few examples.

DPC Flexible Polythene
Roles of D.P.C. come in a range of widths from 110 to 300mm and supplied in lengths of 8 to 30m
Specialist types of flexible D.P.C. are also available in lead and copper coated with bitumen to prevent any corrosion and staining of the face brickwork which are more expensive.
Flexible D.P.C. is laid on to a fresh bed of mortar approximately 5mm thick and should cover the whole length and width of the wall.
The mortar bed should be free from stones that could penetrate the flexible D.P.C. causing rising damp through the rest of the internal or external leaf.
Placing the D.P.C. roll at one end of a wall, gently unrolled and pressed into the mortar using the back of the Brick Trowel so that the D.P.C. adheres to the mortar bed.
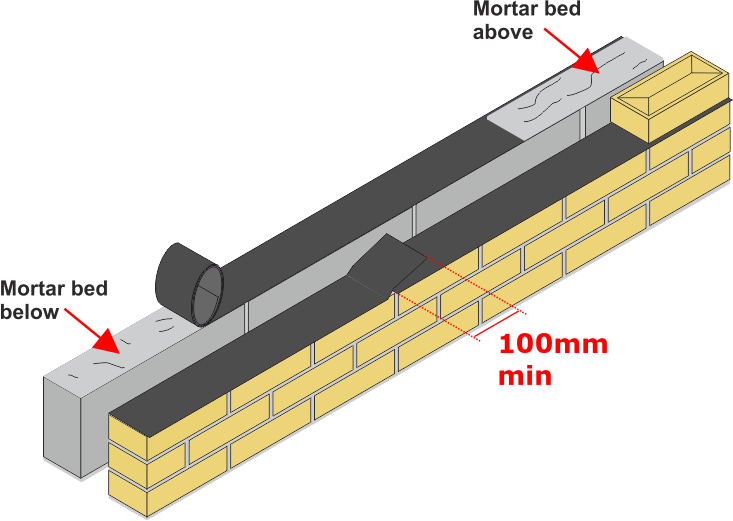
Overlapping or change in direction in a leaf the D.P.C. must overlap a minimum of 100mm or width of the D.P.C.
Ensure that the D.P.C. does not go into the cavity space causing obstruction and D.P.C. external edges are visible and not bridged by the mortar when completing the pointing.
The bed mortar which is underneath the flexible D.P.C. should have a flush finish with the flexible D.P.C. extending from the face of the wall.

Storing DPC

• Store rolls of DPC correctly.
• Stack rolls on end, no more than three rolls high.
• Rolls of D.P.C. that are stored flat are prone to distortion which can make them difficult to lay.
• If possible store at an even temperature.
• Ensure that bitumen and other thermoplastic materials are not in contact with any direct heat source.
• Since some D.P.C. materials may become stiff in cold weather conditions, store sufficient rolls for the next day’s use in a warm place overnight.
• Check the labels on adhesives for any storage requirements, eg avoidance of high or low temperature, and for any hazards relating to solvent vapours.

Storage and Handling
In all cases follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for storage and handling.
For additional information on this topic click on the links below
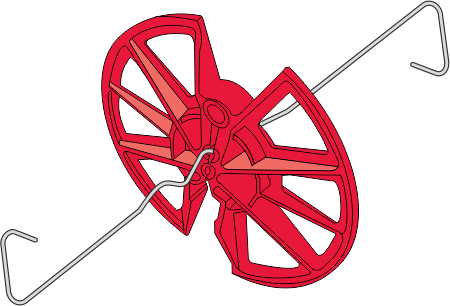
Universal Insulation Retaining Clip
Heavy Duty Wall Tie
Checking Wall Ties
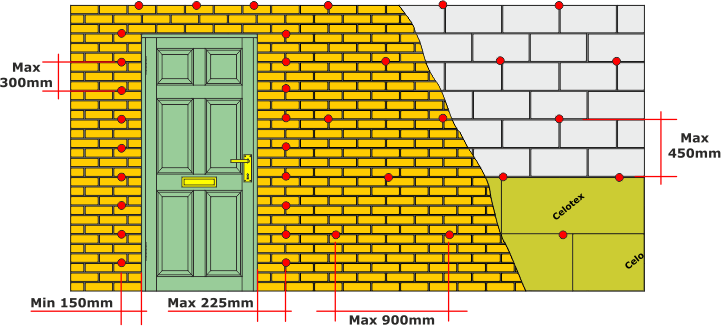
Wall ties should be placed 900mm maximum horizontally the vertical distance should be no more than 450mm horizontally in a wall with no openings in the cavity.
Cavity walls with openings should have a horizontal wall tie more than 150 mm maximum from the edge of the opening vertical spacings is no more than 225mm.
For strength, all ties must be bedded at least 50mm into each wall leaf and the tip of the wall ties should be in the centre of the cavity wall facing downwards.
Checking Wall Ties
Wall Ties Position
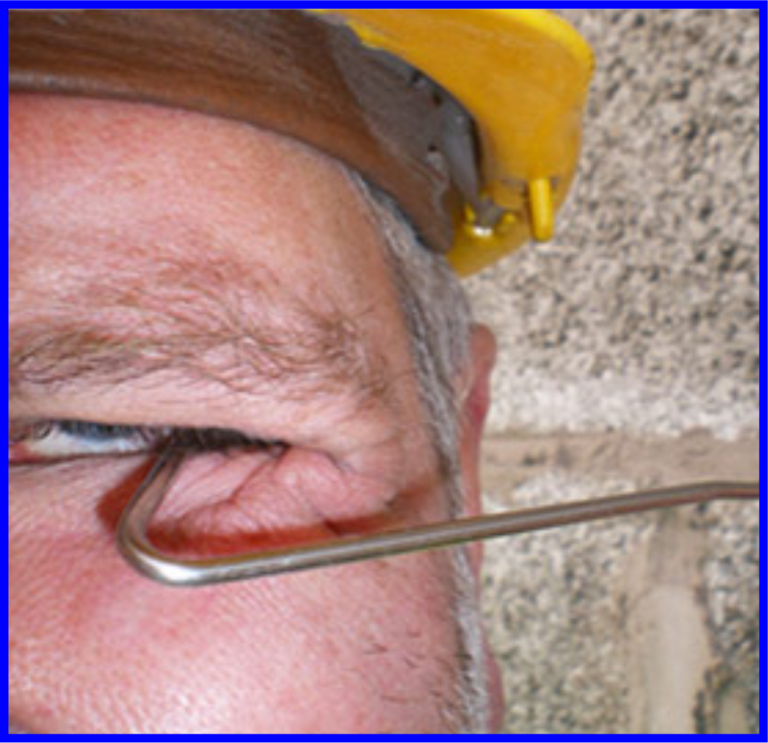
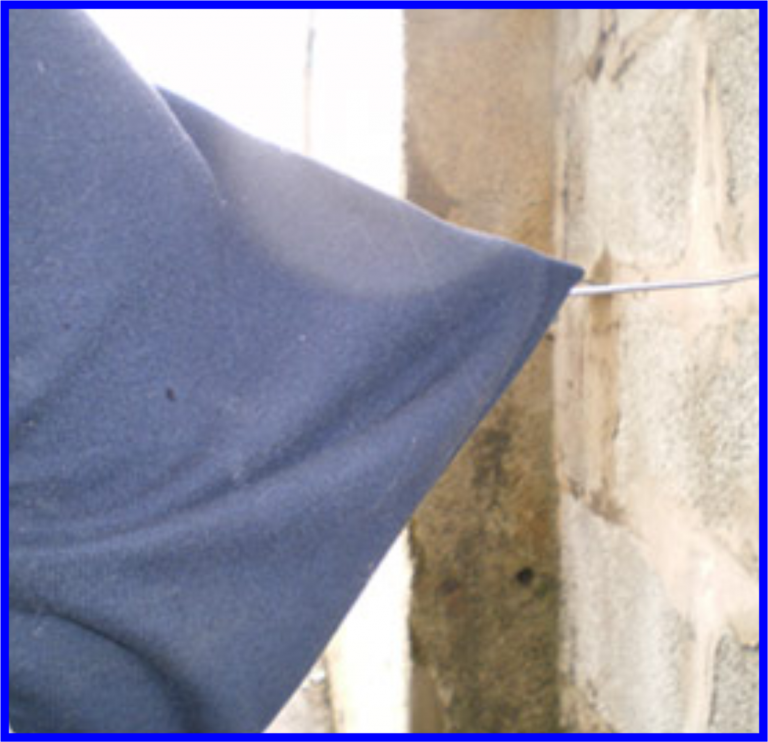


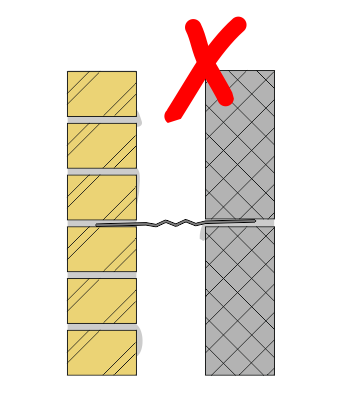
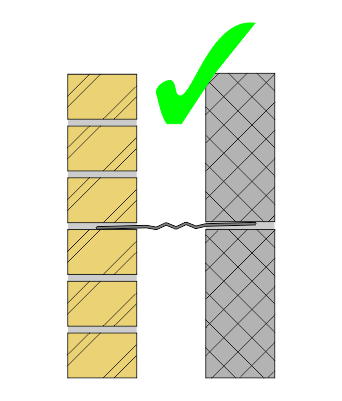
There is a risk of injury if wall ties are left protruding from a single wall leaf before the second leaf is constructed.
Site managers should make all workers and visitors aware of this risk.
To reduce the risk of injury, Ancon’s stainless steel wall ties feature rounded safety ends and Ancon TeploTie
wall ties are supplied with bright plastic end caps.
These end caps should be applied loosely to the outer end of a TeploTie as work on the first leaf progresses; the caps must then be removed before the tie is built into the second leaf.
Ancon recommends both leaves of a cavity wall are built simultaneously to eliminate this risk.
For additional information on this topic click on the links below
Mortar is a mixture of materials for jointing masonry units.
The basic materials are cement, sand and water, but other materials such as lime or air-entraining agents (plasticisers) may also be used to improve working properties and durability.
The purpose of the cement is to bind each particle together when water is added.
Coarse sand is not used for mortar because it is less workable, less smooth and does not produce as neat a finish when pointed.

Selection of Cement Bags
Sand is often referred to as a fine aggregate.
It is normally dug from a pit or a quarry and should be clean and free from impurities.
Sea sand contains salt, which will adversely affect the mortar and should not be used unless it has been washed and supplied by a reputable firm.
Good mortar sand should be well graded so that it contains a mixture of fine, medium and coarse particles.
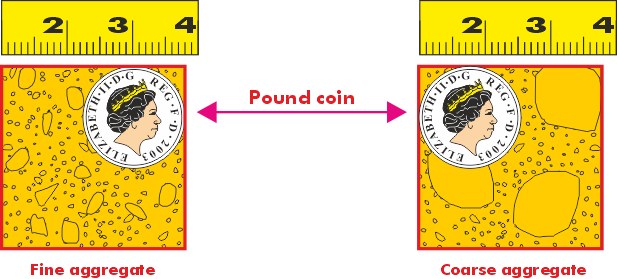
Sand Sizes

Mortar Staines
If the mortar has a high content of water, when laying bricks the mortar will cause runs of water on the face of your brickwork.
The bed mortar joints reduce in size due to the weight of brick or block courses above and your face work will not be to gauge.
Water saturated bricks will have the same issue as above this is why it’s important to Stack and Store your Bricks Correctly.
Have similar compressive strength to the bricks or blocks.
It should not be stronger than is necessary to provide masonry of adequate strength to meet structural and durability requirements.
Have adequate tensile strength to support flexural and shear loads.
Have good frost resistance and resist water penetration in external situations.
Not detract from the appearance of the brick or block.

Hang on the trowel and spread easily.

Mixing Mortar