
Teaching and learning resources for the construction industry with NVQ and Diploma Assessment Criteria
The learner will:
1. know how to prepare for and lay
short lengths of a path using paving slabs.
The learner will:
1. know how to prepare for and lay short lengths of a path using paving slabs.


Sandstone Paving Slabs

Old Riven Paving Slab
There is a wide selection of concrete slabs as the name suggests a mixture of fine and coarse aggregates which are mixed with cement and coloured dyes.
The different shapes and patterns are created by casting concrete into moulds shapes then either pressed or vibrated to give strength to the slab then allowed to dry.
The most common size of concrete slab size is 450x450x38mm this is a manageable size for lifting by one person, with the largest size slabs requiring two people and lifting aid.
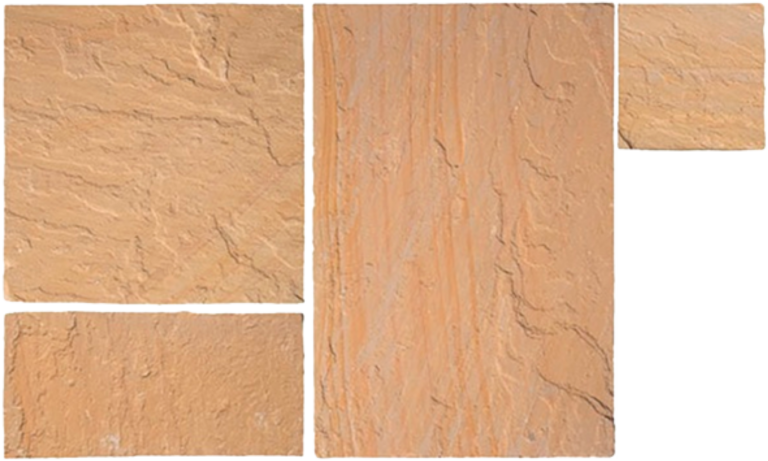

Sandstone Paving Slabs
Sandstone Paving Slabs are made up of grains of sand held together by a silicon based ‘cement’.
It’s this ‘cement’ that gives the sandstone is various colours, textures and toughness.
The weaker this cementitious material is, the worse quality of the stone.
These paving slabs come in various sizes which can be integrated to form a semi-random pattern.
Natural Stones Paving slabs are comprised of a variety of natural stone including granite, marble, limestone, sandstone and slate.
Stone slabs tend to be thicker and with either regular shapes or almost rectangular in shape.
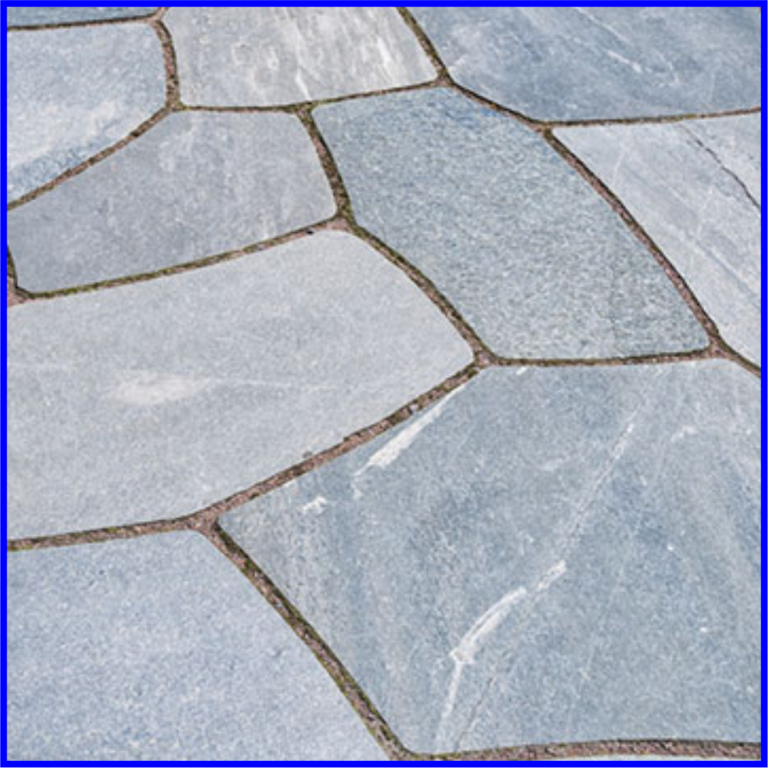

Natural Stones Paving

Porcelain Paving Slabs
Porcelain Paving Slabs made with a mixture of clay, sand and other minerals are placed into a high-temperature kiln which produces a durable and non-porous material.
The Porcelain Paving Slabs are resistant to water absorption ensures that porcelain paving requires very little maintenance.
This type of slab laying is known as porcelain paving.
These paving slabs come in various sizes which can be integrated to form a semi-random pattern.
Natural Stones Paving slabs are comprised of a variety of natural stone including granite, marble, limestone, sandstone and slate.
Stone slabs tend to be thicker and with either regular shapes or almost rectangular in shape.
Aggregate Bays
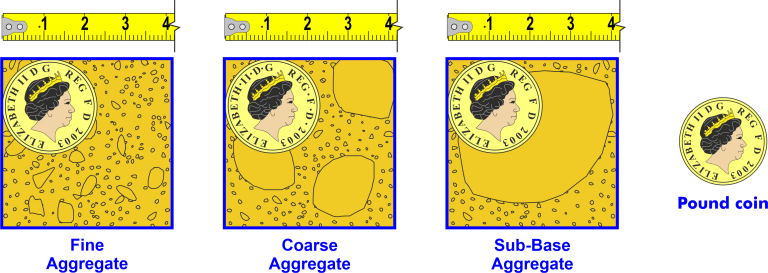
Aggregates
Fine Aggregate describes the natural sand, crushed stone sand or similar, which pass through a 5mm sieve.
Coarse Aggregate describes materials such as natural gravel, crushed gravel or crushed stone that is retained on a 5mm sieve.
The usual coarse aggregate used in concrete is 20mm down to 10mm.
Sub-Base Aggregate describes the natural sand, crushed stone sand or similar, which pass through a 40mm sieve.
Sub-bases are the load-bearing layer of many pavements, the buried component that provides strength and resilience.
They can also provide drainage, with the right choice of aggregate, but their key role is to provide that firm, stable and reliable foundation for the prettier parts of the pavement.

Hydrated Lime
Lime mortar they’re generally referring to mortar made with hydraulic lime or fat lime putty, sand with no cement.
Your training centre will more than likely use hydra lime instead of cement this enables the training centre to reuse all the materials in your bricklaying assessment.
Lime mortar does not set hard which is ideal for teaching practical activities in brickwork.
Bricklayers require a mortar mix which is described as ‘fatty’.
This means it hangs on the trowel without being sticky, it spreads easily and it does not stiffen too quickly or too slowly.
The mortar should meet other requirements to ensure that it retains its strength and durability during the life of the brickwork or blockwork.

Selection of Cement Bags
Additional information on this subject can be found at the following links: